**Understanding How Car Brakes Work: A Comprehensive Guide**
When you press the brake pedal, you expect your vehicle to come to a stop safely and smoothly. But have you ever wondered what happens behind the scenes? How do car brakes actually work? Let’s dive into the mechanics of braking systems to understand how this crucial safety feature operates.
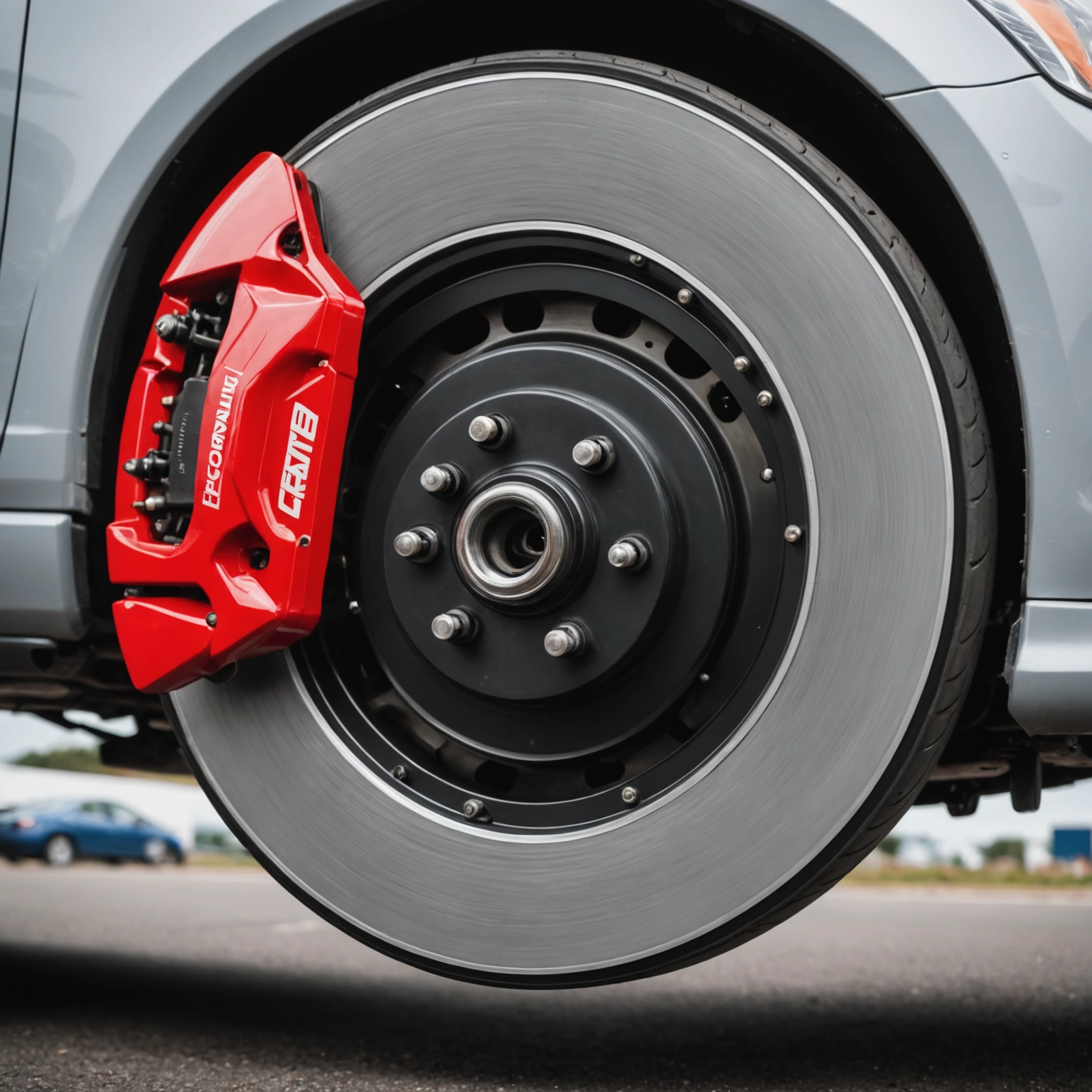

### The Basics of Car Brakes
Car brakes are designed to slow down or stop a vehicle by converting kinetic energy—the energy of motion—into a form that can be safely dissipated. The primary components involved in most modern braking systems are:

– **Brake Pedal**
– **Master Cylinder**

– **Brake Lines**
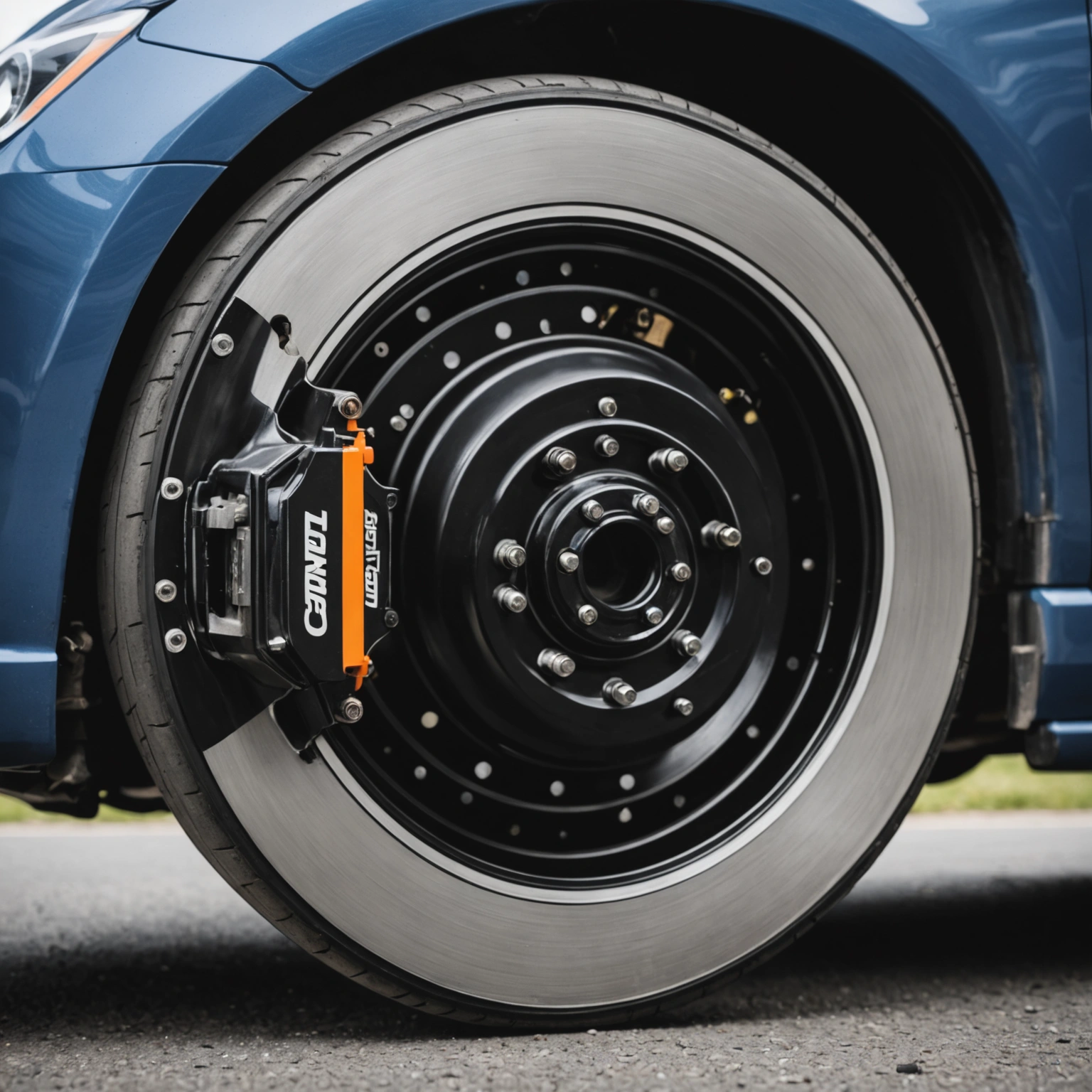
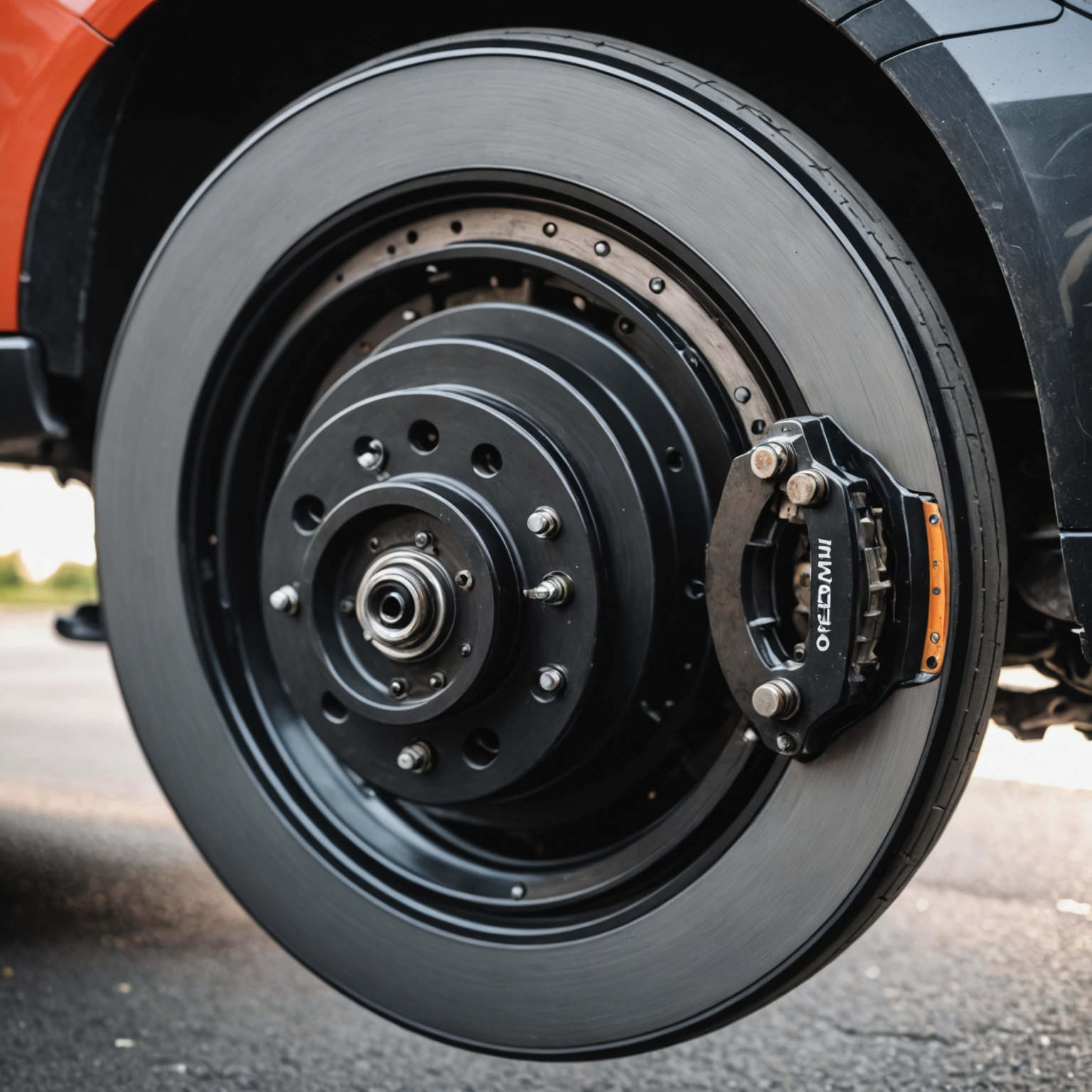
– **Brake Calipers and Wheel Cylinders**
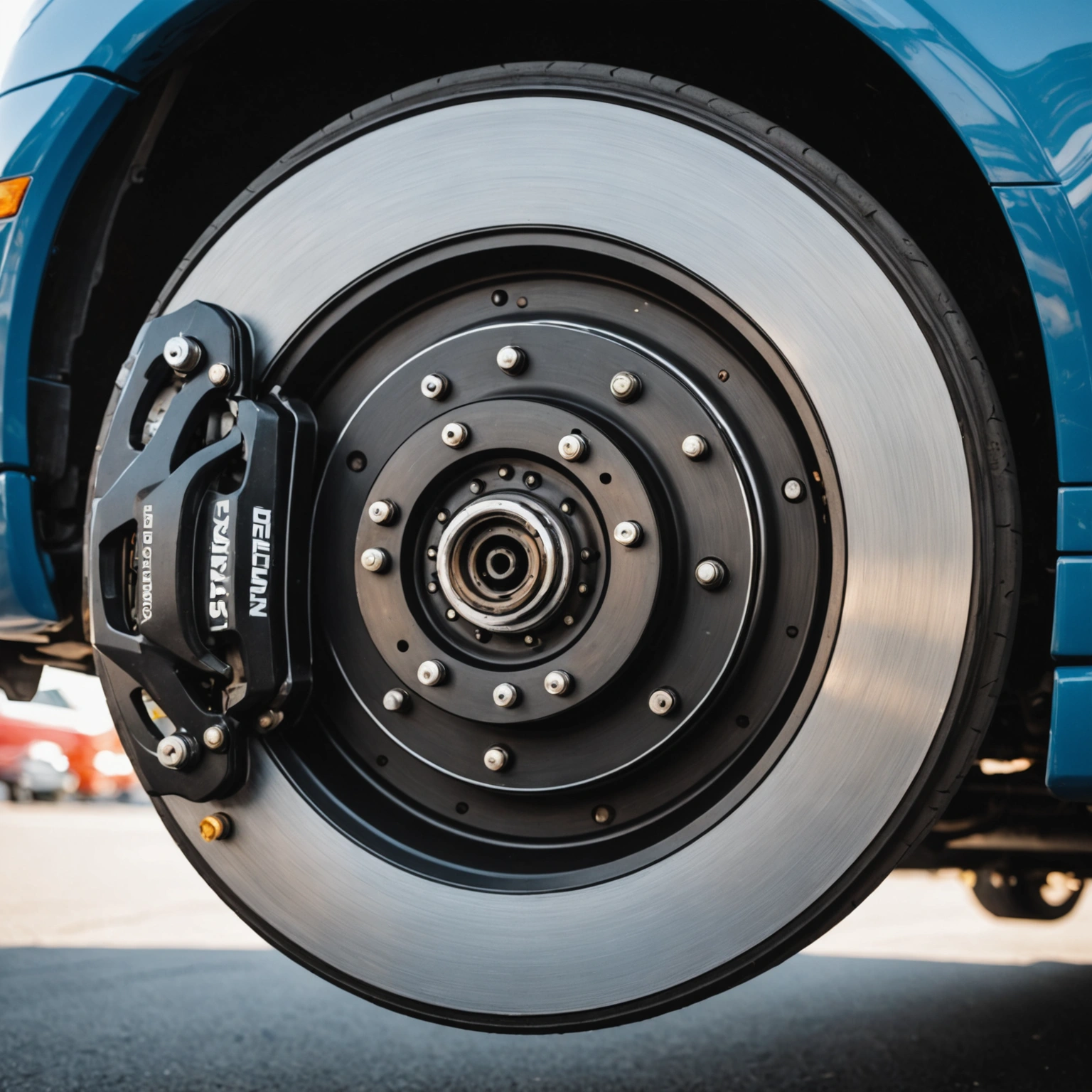

– **Brake Pads and Shoes**
– **Rotors and Drums**
### How the Braking Process Works
1. **Pressing the Brake Pedal:**
When you press the brake pedal, it acts as a lever that pushes a piston inside the master cylinder. This action pressurizes the brake fluid in the hydraulic system.
2. **Hydraulic Pressure Transmission:**
The brake fluid, which is incompressible, transmits this pressure through brake lines to the brake calipers (for disc brakes) or wheel cylinders (for drum brakes).
3. **Engaging the Brake Components:**
– In **disc brakes**, the hydraulic pressure causes the calipers to squeeze the brake pads against the spinning rotor.
– In **drum brakes**, the pressure pushes the wheel cylinders outward, forcing brake shoes against the inside of the drum.
4. **Friction and Deceleration:**
The contact between brake pads and rotors (or shoes and drums) creates friction. This friction opposes the rotation of the wheels, converting the vehicle’s kinetic energy into heat.
5. **Heat Dissipation:**
The heat generated by friction is dissipated into the air. Proper ventilation and materials are essential to prevent overheating, which can reduce braking effectiveness.
### Types of Brake Systems
– **Disc Brakes:**
Commonly found on the front wheels and increasingly on the rear, disc brakes are known for their efficient heat dissipation and consistent performance.
– **Drum Brakes:**
Older designs mostly on the rear wheels, drum brakes are enclosed and can be more prone to heat build-up but are cost-effective.
– **Anti-lock Braking System (ABS):**
Modern vehicles incorporate ABS, which prevents wheel lock-up during hard braking, maintaining steering control by modulating hydraulic pressure rapidly.
### Maintenance and Safety
Regular inspection of brake pads, rotors, and fluid levels is vital. Worn brake pads or contaminated brake fluid can impair braking performance, increasing stopping distances and safety risks.
### Conclusion
Understanding how car brakes work helps appreciate their importance in vehicle safety. They rely on hydraulic pressure, friction, and precise engineering to bring your vehicle to a stop efficiently. Proper maintenance ensures that your braking system continues to function flawlessly, keeping you safe on the road.
—
**Stay safe and drive responsibly!**