**Understanding How Automotive Alternators Work: A Comprehensive Guide**
When you turn on your vehicle’s ignition and see the dashboard lights brighten, or when your phone charges via the USB port, you’re witnessing the power of the alternator in action. But have you ever wondered exactly how this vital component keeps your car running smoothly? In this blog post, we’ll explore the inner workings of automotive alternators, explaining how they generate electrical power to keep your vehicle’s systems operational.

### What Is an Alternator?
An alternator is a type of electrical generator specifically designed for vehicles. Its primary role is to produce electricity to power the car’s electrical systems—like lights, radio, and onboard computers—and to recharge the battery, ensuring the vehicle can start reliably each time.

### Basic Principles of Alternator Operation
At its core, an alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. It operates on the principles of Faraday’s Law, which states that a changing magnetic field within a coil induces an electric current.
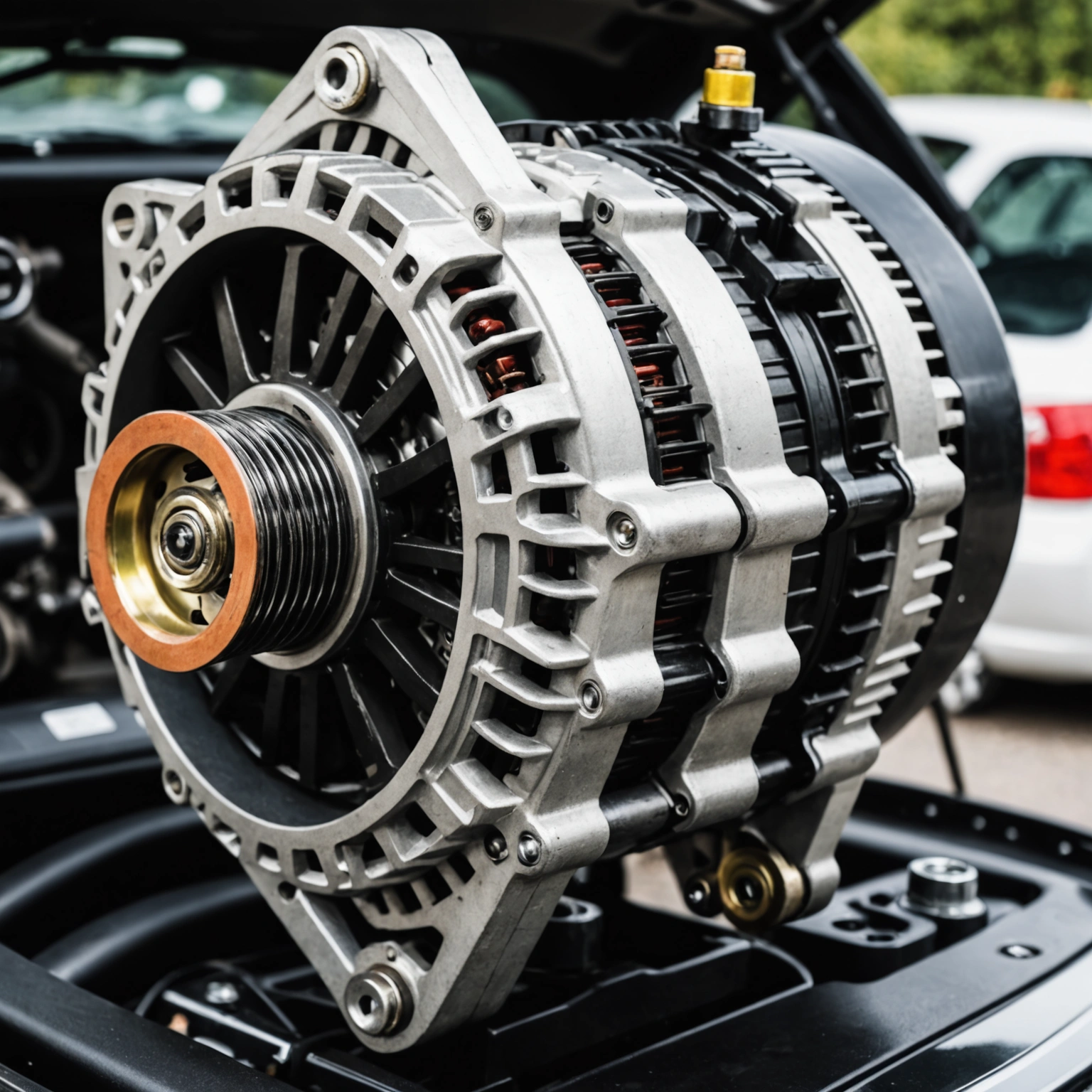

### Key Components of an Automotive Alternator
1. **Rotor (Field Coil):** The rotating part that creates a magnetic field.
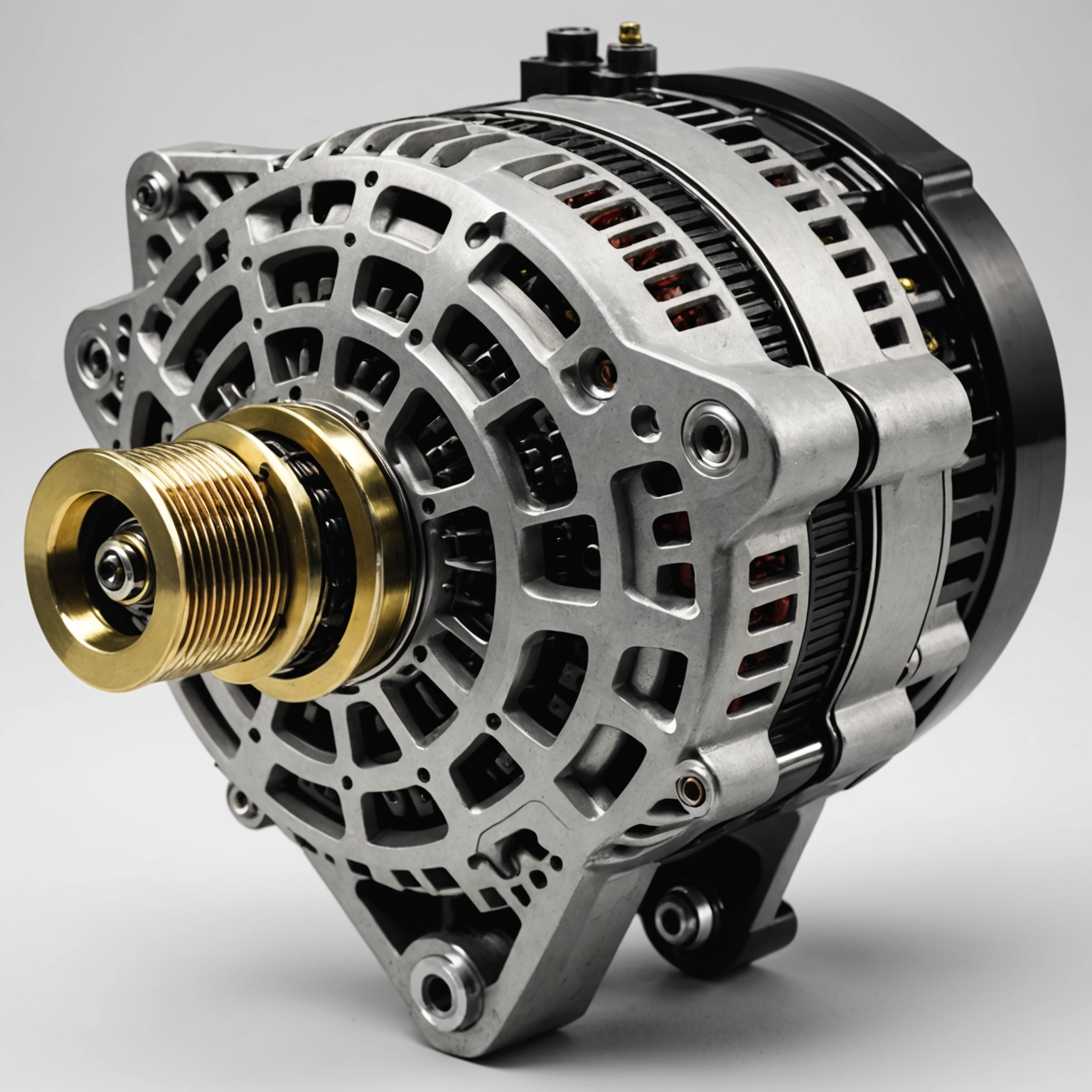

2. **Stator:** The stationary part that contains wire coils where electricity is generated.
3. **Rotor Bearing and Shaft:** Support the rotor and allow it to spin smoothly.
4. **Voltage Regulator:** Controls the output voltage to match the vehicle’s electrical system requirements.
5. **Rectifier (Diodes):** Convert the alternating current (AC) produced into direct current (DC) used by the vehicle’s systems.
6. **Pulley and Belt System:** Connects the alternator to the engine’s crankshaft via a belt, transferring mechanical energy.
### How Does an Alternator Work?
Here’s a step-by-step overview of the alternator’s operation:
1. **Mechanical Energy Conversion:**
The engine’s crankshaft drives the alternator’s pulley through a belt. As the engine runs, it spins the pulley, which in turn rotates the rotor inside the alternator.
2. **Creating a Magnetic Field:**
The rotor contains a coil of wire (the field winding) energized by a small amount of current supplied through slip rings and brushes. This current generates a magnetic field around the rotor.
3. **Electromagnetic Induction:**
As the rotor spins inside the stator’s stationary coils, the changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the stator windings. This is the core process of electromagnetic induction.
4. **AC Electricity Generation:**
The induced voltage in the stator is alternating current (AC). Since most vehicle electrical systems operate on direct current (DC), the AC output must be converted.
5. **Rectification and Voltage Regulation:**
The alternator contains diodes (rectifier) that convert AC to DC. The voltage regulator monitors the output voltage and adjusts the current supplied to the rotor’s field coil, controlling the magnetic field strength to keep the voltage within a specified range (usually around 13.5 to 14.8 volts).
6. **Supplying Power and Charging the Battery:**
The DC electricity is then distributed to power the vehicle’s electrical systems and recharge the battery, ensuring a steady supply of power during engine operation.
### Why Is the Voltage Regulator Important?
Without a voltage regulator, the alternator could produce excessively high voltage, potentially damaging sensitive electronics, or too low voltage, leading to insufficient power. The regulator maintains a consistent voltage, adapting to varying electrical loads and engine speeds.
### Summary
In essence, the automotive alternator is a sophisticated device that harnesses the engine’s mechanical energy to generate electrical power. Through electromagnetic induction, rectification, and regulation, it ensures your vehicle’s electrical systems function seamlessly and the battery remains charged.
Next time you start your car or notice the dashboard lights up, remember the vital role played by your alternator in keeping your vehicle alive and well.